Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: 2024

Achievements, Impacts, Drawbacks, and Future Projections
In 2023, an estimated 94% of healthcare companies employed artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning in some way.1 That said, AI technology can be a controversial or polarizing topic – some people love it while others hate it. No matter where you fall on this spectrum, understanding both the advantages and drawbacks of AI can be beneficial for healthcare organizations when deciding when and when not to use this technology, as well as how to use it responsibly.
To help with this, we discuss the pros and cons of AI in healthcare. We also talk about how this technology has impacted the healthcare industry, what its usage looks like today, and what we may expect to see in the future. We then wrap things up by providing steps healthcare organizations can take to better prepare their employees to stay current with this and other technological advancements.
Advantages of AI in Healthcare
When used in healthcare settings or for health-related needs, AI has the potential to provide many benefits. For healthcare professionals, it can assist with patient diagnosis, predict disease spread, and aid in the customization of treatment plans.2 AI can also aid in the performance of certain administrative functions.
Administrative benefits of AI in healthcare include:3
- Allowing for the automation of certain tasks, freeing up healthcare workers to perform other duties or to spend more time one-on-one with patients
- Reducing involvement with simple tasks, such as answering a patient’s medication-related question or scheduling an appointment with their provider
- More easily identifying billing or insurance claim patterns that might be suspicious or unusual, suggesting that fraudulent activity may be occurring
AI also offers benefits for individuals utilizing the healthcare system. According to research, it can improve the accuracy of care a patient receives while being efficient and accessible.4
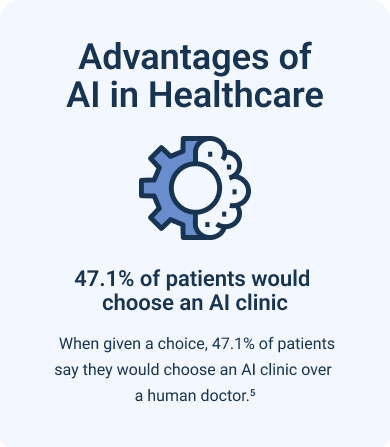
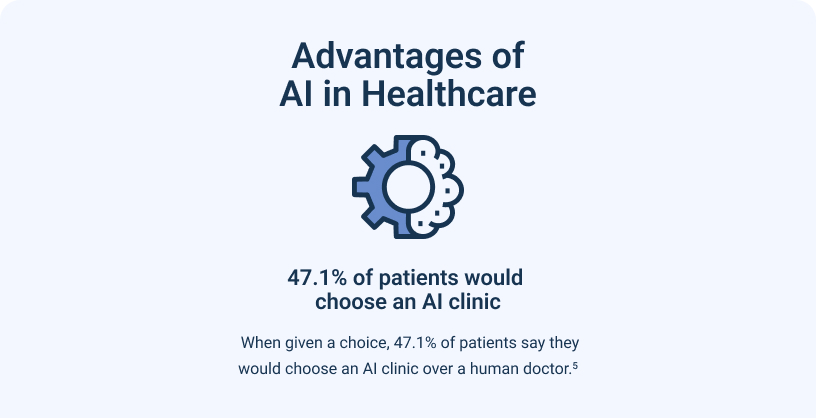
AI might be extra beneficial for patients taking medications. In one study, subjects using insulin pens and inhaler devices were monitored by human observers. These observations were then used to create AI-based solutions. The AI technology developed detected when the pens and inhalers were used and whether the patient took the appropriate steps afterward. Thus, this type of solution could improve medicine safety and reduce oversight needed by a healthcare team.6
Potential Drawbacks of Health-Related AI
Despite offering many advantages within a healthcare context, AI doesn’t come without its challenges. One is its potential for inaccuracy.
If a person uses AI for a more personalized shopping experience, if the technology is wrong about the item the person wants, it’s not a major deal. It may be frustrating, but it isn’t the end of the world. If, however, AI is inaccurate when diagnosing or treating patients, the stakes are much higher. Mistakes made in healthcare can lead to “devastating consequences for the patient who is the victim of the error.”7
Another concern surrounding the use of AI by healthcare organizations or facilities is data security. Electronic health record (EHR) systems contain some of a patient’s most important and most private information. This makes them a common target for hackers interested in obtaining unauthorized information.8


When a healthcare organization’s data is breached, the consequences can be devastating. There can be an erosion of patient trust and confidence, the organization’s reputation may be damaged (sometimes beyond repair), and financial losses can be in the hundreds of millions of dollars when both direct and indirect data breach costs are considered.10
AI’s Impact on the Healthcare Industry
In addition to considering the pros and cons of using AI technology in the healthcare industry, it’s important to also look at its effects. One way to quantify these effects is financially.
If a health insurance claim is not filed correctly, the carrier can deny reimbursement. AI-powered solutions can help identify these errors before the claim is submitted, leading to higher reimbursement rates. This can reduce operational costs for healthcare providers, also improving claim processing efficiency while helping ease cash flow issues.11


Another financial consideration is whether AI can help reduce patient healthcare costs. Some suggest that it can. For example, a public hospital in Atlanta reported that it saved $4 million over a two-year period by using an AI-enabled tool that identified “at-risk” patients, reducing readmission rates by 31%.12
The use of AI technology may also impact how healthcare professionals provide patient care. Providers may use AI applications to:
- Help diagnose patients or decide treatment methods
- Educate patients about their conditions or treatment plan
- Measure adherence to treatment protocol
- Provide support between healthcare appointments
In this way, AI has the ability to alter healthcare as we’ve traditionally known it. As artificial intelligence technology is created and continues to be updated, practitioners are exposed to a broad variety of applications that could make their roles easier to perform while enabling them to provide better, more personalized patient care.12
Where We Stand with AI in Healthcare
On October 19, 2023, the World Health Organization issued a news release indicating that it had published considerations for regulating AI for health. This publication was intended to stress not only how important it is to establish the safety and effectiveness of AI but also to hasten AI system accessibility to those in need and further conversations between parties with interests in these applications – which includes AI developers and product manufacturers, along with healthcare workers and patients.
Some of the advice provided by the WHO included:13
- Documenting AI use and being transparent with this documentation to help foster trust
- Comprehensively addressing how AI will be used, particularly to help minimize its vulnerabilities
- Validating data externally and providing clear AI usage instructions to support its safety and regulation
- Rigorously analyzing AI systems to reinforce data quality and reduce the risk of biases or errors
- Understanding how to use AI while protecting patient confidentiality, such as required by HIPAA
- Continuing collaborative efforts between everyone involved to ensure regulatory compliance
During 2023, at least half of the states in the U.S. introduced legislative bills surrounding artificial intelligence, including bills introduced in both the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico, with several either adopting resolutions or enacting AI legislation.14 Some of these bills were designed to establish policies and procedures for AI implementation and utilization. Others created advisory councils to better understand and monitor AI systems developed.
The Future of AI: What Can the Healthcare Industry Expect in 2024 and Beyond?
Like with any technology, AI continues to evolve. New applications are developed to solve common problems or improve processes. Older technology is updated to improve functionality or address known vulnerabilities or challenges. Both are a strong indicator that AI is here to stay.
What is less clear is what the healthcare industry will look like five, 10, or 50 years from now because of AI usage. The World Economic Forum suggests that its global impact is dependent upon three important factors:16
- Whether the technology is developed with both representative and usable data
- Whether the AI can be trusted, which requires that it be deployed responsibly, transparently, and competently
- Whether it fits seamlessly into current workflows while also being easily scalable
Over time, a clearer image will emerge. Other advantages of AI may be discovered, as may additional drawbacks. Closing the gaps between the two is important to creating technology in which the advantages outnumber the disadvantages, or — in terms of patient health — the benefits outweigh the risks.
Help Prepare Healthcare Workers for Technological Advancements
Regardless of exactly what the future looks like from an AI standpoint, it’s important for healthcare professionals to be aware of the technology used in the course of their daily tasks. Knowing how to use technology correctly can improve worker productivity and efficiency, also improving patient safety.17 And that’s where training and upskilling can play an important role.
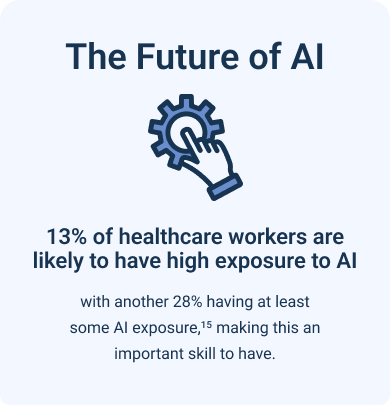
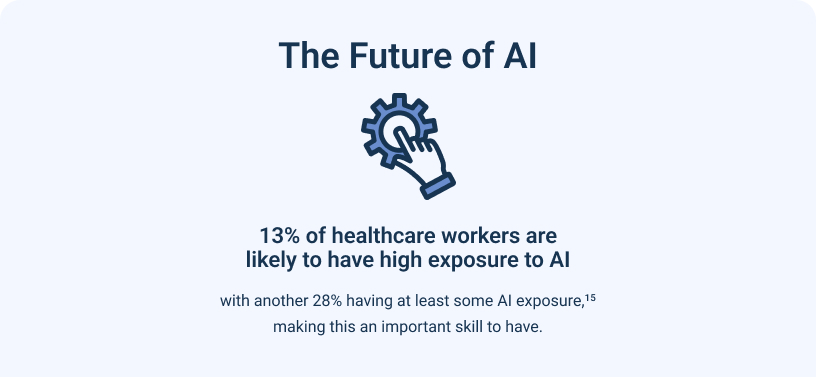
13% of healthcare workers are likely to have high exposure to AI, with another 28% having at least some AI exposure, making this an important skill to have.18
Providing healthcare employees access to up-to-date training programs helps ensure that they have the knowledge, skills, and comfort level needed to properly and effectively utilize all “tools” relevant to their positions. Upskilling programs can expose learners to current methodologies, techniques, and best practices within the healthcare industry.
This information also helps prepare workers to use the technology that they’re likely to encounter within their respective positions. This is especially critical for employees who lack the skills needed to interact with digital devices and systems.


Nasium Training Offers Customized Healthcare Training Solutions
While Nasium Training does not provide training specific to AI technology and tools, we do offer healthcare organizations access to a variety of training solutions for their employees. These training solutions can be customized based on your individual skills gaps and needs.
Nasium Training solutionsare available for both clinical and non-clinical healthcare workers. Most are offered entirely online, providing learners the opportunity to gain the information they need at a time that fits their schedule best.
When you partner with Nasium Training, your employees gain access to:
- Experienced instructors
- An intuitive learning platform
- Personalized training
To learn more about how we can help train your healthcare workforce, contact us today. We’d love to learn about the challenges you face, then work together to solve those challenges through upskilling, reskilling, and/or cross-skilling your top talent.
1 Morgan Stanley. How Artificial Intelligence Could Reshape Health Care. https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/ai-in-health-care-forecast-2023
2 Secinaro S, et al. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A Structured Literature Review. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12911-021-01488-9
3 IBM. The Benefits of AI in Healthcare. https://www.ibm.com/blog/the-benefits-of-ai-in-healthcare/
4 Rajpurkar P, et al. AI in Health and Medicine. Nature Medicine. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01614-0
5 Robertson C, et al. Diverse Patients’ Attitudes Towards Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnosis. PLoS Digital Health. https://journals.plos.org/digitalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pdig.0000237
6 Zhao M, et al. Assessment of Medication Self-Administration Using Artificial Intelligence. Nature Medicine. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01273-1
7 Naik N, et al. Legal and Ethical Consideration in Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Who Takes Responsibility? Frontiers in Surgery. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsurg.2022.862322/full
8 khan B, et al. Drawbacks of Artificial Intelligence and Their Potential Solutions in the Healthcare Sector. Biomedical Materials & Devices. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s44174-023-00063-2
9 The HIPAA Journal. Healthcare Data Breach Statistics. https://www.hipaajournal.com/healthcare-data-breach-statistics/
10 Medical Group Management Association. Managing the Impact of Healthcare Data Breaches on Your Organization. https://www.mgma.com/articles/managing-the-impact-of-healthcare-data-breaches-on-your-organization
11 Johnson M, et al. Responsible Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Predicting and Preventing Insurance Claim Denials for Economic and Social Wellbeing. Information Systems Frontiers. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10796-021-10137-5
12 Lee D, No Yoon S. Application of Artificial Intelligence-Based Technologies in the Healthcare Industry: Opportunities and Challenges. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/1/271
13 World Health Organization. WHO Outlines Considerations for Regulation of Artificial Intelligence for Health. https://www.who.int/news/item/19-10-2023-who-outlines-considerations-for-regulation-of-artificial-intelligence-for-health
14 National Conference of State Legislatures. Artificial Intelligence 2023 Legislation. https://www.ncsl.org/technology-and-communication/artificial-intelligence-2023-legislation
15 Pew Research Center. Which U.S. Workers are Most Exposed to AI on Their Jobs? https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2023/07/26/2023-ai-and-jobs-appendix/
16 World Economic Forum. Why and How We Must Accelerate AI’s Impact on Global Health. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2023/01/ai-impact-on-global-health-davos23/
17 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Technology as a Tool for Patient Safety. https://psnet.ahrq.gov/perspective/technology-tool-improving-patient-safety
18 Pew Research Center. Which U.S. Workers are Most Exposed to AI on Their Jobs? https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2023/07/26/2023-ai-and-jobs-appendix/
19 Eddy N. Survey: Healthcare Struggles with Persistent Tech Skills Shortage. MobiHealthNews. https://www.mobihealthnews.com/news/survey-healthcare-struggles-persistent-tech-skills-shortage
